Binders and Longevity: The Science Behind Activated Charcoal, Clays, and Toxin Defense

In a world filled with microplastics, industrial pollutants, and persistent organic toxins, the body’s natural detoxification systems face constant overload. While the liver and kidneys perform most of this work, a lesser-known tool—binders—can offer vital support. Compounds like activated charcoal, bentonite clay, zeolite, and chlorella have been used for centuries to neutralize toxins, bind heavy metals, and protect cellular health. Modern research now suggests these natural detoxifiers may also play a role in longevity by reducing systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, and toxin burden over time.
Detoxification and Longevity
The body’s detoxification process depends heavily on liver phase I and II enzymatic activity, bile flow, and efficient toxin excretion through the intestines. However, many environmental toxins—especially lipophilic compounds such as pesticides, flame retardants, and plasticizers—can reabsorb into circulation through enterohepatic recirculation.
That’s where binders come in.
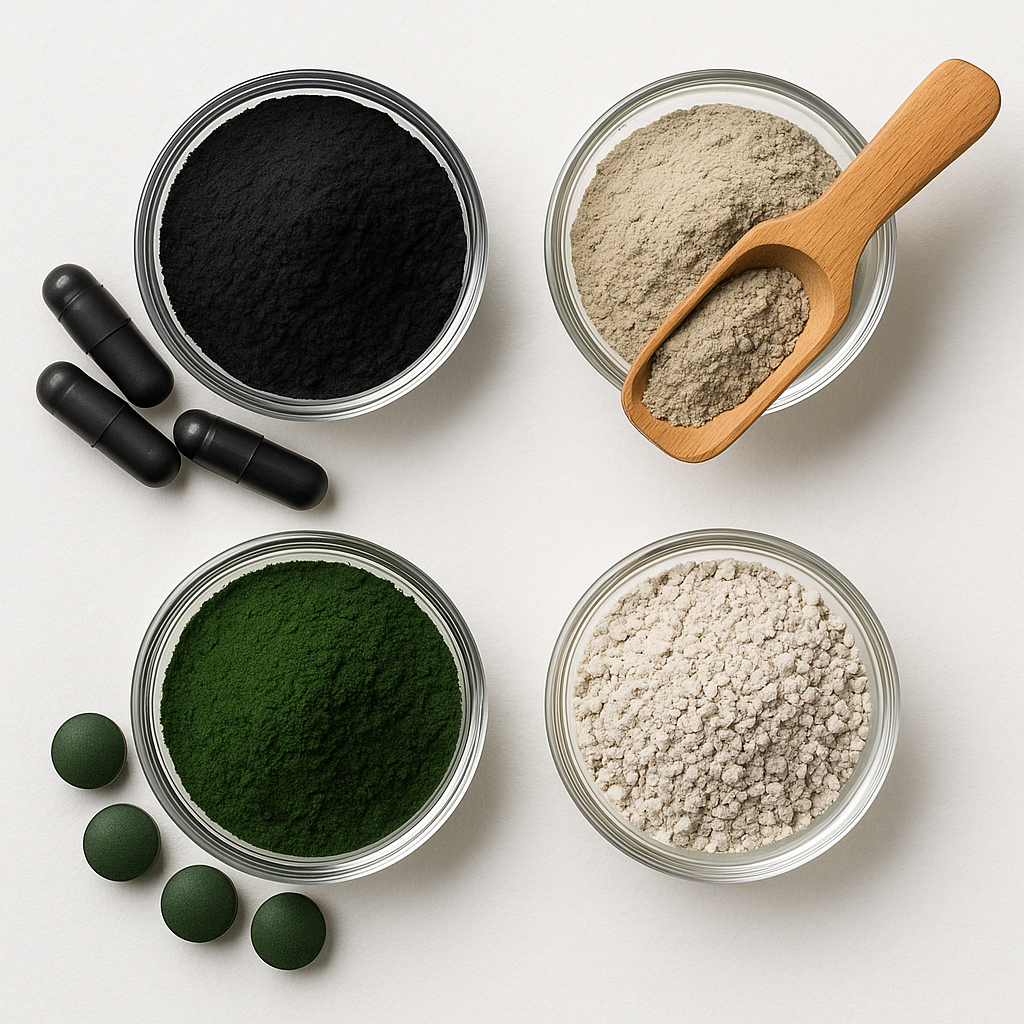
Activated charcoal, derived from carbon-rich materials, works through adsorption, trapping toxins in its porous surface and preventing reabsorption. Studies show that it can bind mycotoxins, bacterial endotoxins, and even certain pharmaceutical residues. Similarly, bentonite clay, a natural montmorillonite clay, carries a strong negative charge that attracts positively charged heavy metals like lead and mercury. Zeolite, a volcanic mineral with a crystalline lattice structure, operates on the same principle, binding heavy metals and ammonia through ion exchange.
By intercepting these harmful compounds before they enter the bloodstream, binders reduce cellular stress and mitochondrial toxin exposure—a key mechanism in slowing biological aging. Research links lower toxin burden to enhanced NAD⁺ preservation, reduced oxidative damage, and improved metabolic flexibility—all critical components of healthy longevity.
Gut Health and Inflammation Control
The gut acts as both a filter and a barrier. When compromised, it allows toxins, bacterial fragments, and inflammatory molecules to leak into circulation—a phenomenon known as metabolic endotoxemia. Binders play an indirect but powerful role here.
Activated charcoal and bentonite clay have been shown to adsorb bacterial endotoxins (LPS), reducing their inflammatory signaling in the gut. This lessens the load on the immune system and decreases systemic inflammation—an underlying driver of nearly all chronic disease and aging.
Chlorella, a green microalgae, adds another layer of defense. Unlike mineral binders, chlorella binds organic toxins and heavy metals within the digestive tract while providing antioxidants and chlorophyll to soothe the gut lining. Zeolite complements these effects by supporting microbiome balance through ammonia reduction.
Together, these compounds form a synergistic defense system that supports gut integrity, balances the microbiome, and reduces inflammatory cascades that accelerate aging.
Reducing Everyday Exposure
While detoxification is often associated with cleansing programs, daily exposure management is far more impactful for long-term health. Modern living exposes us to volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pesticide residues, mold mycotoxins, and microplastics—all of which accumulate slowly over time.
Incorporating gentle binders a few times per week, especially after known exposure events—such as travel, poor air quality, or processed food consumption—can provide an ongoing toxin mitigation strategy. For example, taking activated charcoal after a restaurant meal or during illness can reduce absorption of unwanted compounds. Meanwhile, bentonite and zeolite clays support environmental toxin defense without disturbing nutrient absorption when used in moderation.
The longevity benefit lies in lowering the body’s total toxic load—a crucial but often ignored factor in maintaining mitochondrial efficiency, hormonal balance, and immune resilience across the lifespan.
Considerations and Safe Use
While binders offer powerful benefits, their use should be mindful. Because they can also bind medications, supplements, and minerals, it’s best to take them at least two hours apart from food or other nutrients. Hydration is key, as binders rely on water to flush bound toxins from the intestines.
Cycling binders—rotating between charcoal, clay, zeolite, and chlorella—prevents dependency and ensures a balanced detox strategy. For individuals with higher toxin exposure or those undergoing mold or heavy metal protocols, professional guidance is recommended to optimize dosing and duration.
Closing Thoughts
The modern environment constantly challenges our biological resilience. Supporting the body with natural binders isn’t about extreme detox—it’s about equipping the body to handle everyday exposures gracefully. When used intelligently, binders like activated charcoal, bentonite clay, zeolite, and chlorella become powerful allies in the pursuit of cleaner cells, calmer inflammation, and longer life.
Sources
- Efird JT et al., Activated Charcoal Detoxification: A Review of Its Potential Health Benefits and Mechanisms. Journal of Environmental and Public Health, 2020.
- Joshi S et al., Bentonite Clay and Its Applications in Detoxification. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2018.
- Kralj M et al., Zeolites in Medicine: Detoxification and Beyond. Molecules, 2021.
- Merchant R, Chlorella and Heavy Metal Detoxification Mechanisms. Alternative Medicine Review, 2019.
- Fasano A, Leaky Gut and Systemic Inflammation: Clinical Relevance. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology, 2020.
- Wallace DC, Mitochondrial Damage and the Aging Process. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2019.